Key Highlights:
- Staking is a process through which crypto users lock up their crypto assets to secure the network and earn rewards in return.
- Staking can be of two types, liquid staking and locked staking or traditional staking.
- Liquid staking offers flexibility and locked staking ties up capital.
Staking is a process where the crypto holders lock up their tokens to help secure a blockchain network and validate transactions. Here as a form of reward, the holders who have locked up their tokens, are paid in the same cryptocurrency. It is mainly used on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain and it is seen as a more energy-efficient alternative to mining as the entire process consumes very less amount of energy.
Staking as a whole process started back in 2011 as a part of discussions on BitcoinTalk forums. As with mining, the consumption of energy was a huge problem back then, during this forum, the developers were exploring PoS as a way through which they could reduce the energy used. Peercoin was the first project that implemented a hybrid PoW/PoS system in 2012. The concept gained a huge attention around the world after Ethereum made its shift to PoS in 2022 and that’s when PoS started being adopted across modern blockchain networks.
As the adoption across networks grew, this process of staking later evolved into locked staking and liquid staking models. By using either of these technologies the participants were choosing between commitment-based rewards and more flexible yield strategies.
What is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking is a process where users can stake their cryptocurrencies as per Proof-of-Stake mechanism without having to actually lock their tokens away completely. Once the users stake their tokens, they receive a liquid staking tokens (LST) in return, such as the stETH or mSOL. These tokens represent their staked funds and the rewards they earn over time.
The beauty of this process is that with these LSTs, the users can still trade, sell or use them across the DeFi platforms for lending, yield farming or providing liquidity. In this way the user can keep the funds flexible while earning staking rewards.
There are various platforms such as Lido, Jito and Ether.fi that manage more than $25 billion in total value locked. This number indicates the demand for this model. LSTs automatically add rewards over time and they can be exchanged instantly through open markets instead of waiting for long unstaking periods.
By 2026, the liquid staking market is currently growing at a steady pace and market projections estimate a strong growth for liquid staking service through 2032.
What is Locked Staking?
Locked staking or traditional staking, on the other hand, is a process when the users lock their tokens to a validator or a staking pool for a fixed period of time. This period is locked for 7-28 days. During this time, the assets of the users are locked and they cannot be used for anything else. The locked tokens, as the name suggests are locked, cannot be sold, traded or used in any of the DeFi applications.
For staking their cryptocurrencies, users do receive rewards which is typically 3-6% per year. The drawback here is that if the user withdraws earlier than the locking period, then the user can incur penalties or waiting periods before the funds are released.
This model of staking is something that keeps the blockchain networks secure, as validators rely on long commitments from users.
Difference Between Liquid Staking and Locked Staking?
From the above stated two methods of staking, both of them mainly differ in how freely users can use their money, how much they can earn from the staking process and how flexible the process is overall.
As explained above, with liquid staking, users stake tokens like ETH through platforms such as Lido or Jito and receive liquid staking tokens in return. This token represents their staked assets and keeps earning rewards and it can still be traded or used in DeFi for lending, borrowing or providing liquidity.
However, tokens that are staked using a locked staking method cannot be traded on the DeFi once they are staked. Tokens are committed to validators or pools for a fixed time, which is usually 7-28 days. During this time the capital earns only basic staking rewards and cannot be used for other opportunities, even if the markets shifts abruptly or better opportunities come along. Liquid staking removes this problem.
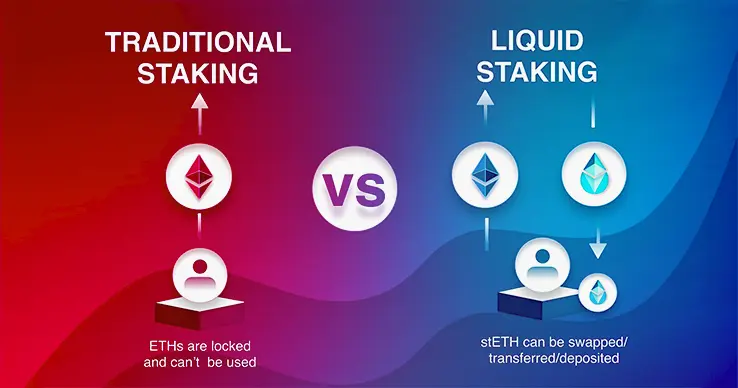
The liquid staking tokens that are received by the users can be sold or used immediately. This means stakers keep earning rewards while still having the freedom to react to market changes. When prices fall, LSTs can be sold instantly instead of being stuck in an unbonding queue. This is how LSTs beat the waiting game and the users can make the most out of the market swings and market opportunities.
Liquid staking allows users to earn extra yield on top of staking rewards, sometimes pushing the returns close to 12% per year, without locking funds for long periods. With locked staking, users usually earn about 3-6% returns annually and users can miss out on market opportunities.
Withdrawals can lead to penalties in locked staking whereas liquid staking offers instant access to the cryptocurrencies and more earning options. As liquid staking provides a great amount of advantages over the locked staking method, it has grown to over $25 billion in value by 2026.
Final Thought
When it is locked staking vs liquid staking, liquid staking wins the battle because it removes the wait. It lets users earn staking rewards while keeping their funds flexible and usable at all times. Compared to locked staking’s idle capital and delays, LSTs offer a smarter, more efficient way to stake in fast-moving crypto markets.
Also Read: Here’s How Solana BTCFi and LSTs are Changing Bitcoin Forever
See less
