Key Highlights
- There are modular blockchains that split tasks like execution and data availability across different dedicated layers.
- The arrival of new hardware and ZK proof have redacted verification times to seconds.
- Ethereum is also preparing for the Glamsterdam upgrade, which will shift validators to ZK proof verification.
The way blockchain networks are developing is going through a major change since the invention of smart contracts, as developers are moving away from all-in-one systems toward dedicated layers that work together like one machine.
There is a new era of modular blockchains taking place in 2026 as the demand for new types of digital ledgers has soared. This development is supported by new architectures and very advanced zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs. These new solutions are providing a solution to scalability problems that have kept blockchain from achieving mass adoption.
According to the experts, modular blockchains and ZK proofs technology are rapidly becoming a part of global-scale usage in finance, gaming, and real-world assets.
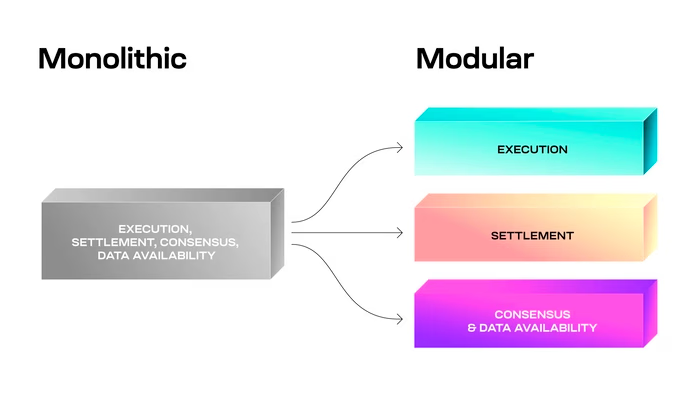
What are Modular Blockchains?
In the past, traditional blockchains like early Ethereum or Solana were developed on monolithic systems. It means that these blockchains manage everything on their single layer, including consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement. While this kind of development provides strong security, it creates a serious problem that creates obstacles to scalability.
(Source: Defiant)
When the activities on the network increase, fees also increase, and the network becomes too expensive for everyday users. On the other hand, if this blockchain goes for upgrades, it might divide the community into two, and it could also go for hard forks. Bitcoin’s 2017 hard fork is the biggest example of this, at block 478,558.
Modular blockchains can provide a solution to this problem. They use a different dedicated layer to perform those important functions, including storing and verifying large amounts of information off-chain while ensuring it can be accessed on-chain at low cost.
Celestia, the first modular data availability layer to go live in 2023, now supports hundreds of rollups and has processed terabytes of data through 2025 and early 2026, all while keeping fees under one cent per transaction.
After this, there are execution layers to handle transaction processing through rollups, which batch thousands of transactions together and post compressed proofs to secure base layers. Settlement and consensus remain on robust Layer 1 networks like Ethereum, which provide finality and dispute resolution. This separation allows each layer to optimize for its specific job without compromising the others.
EigenLayer has introduced another piece through staking, which allows Ethereum stakers to help secure multiple networks at once. This reduces the cost of launching new chains while maintaining strong security guarantees.
Zero-Knowledge or ZK Proofs’ Role in Modular Blockchains
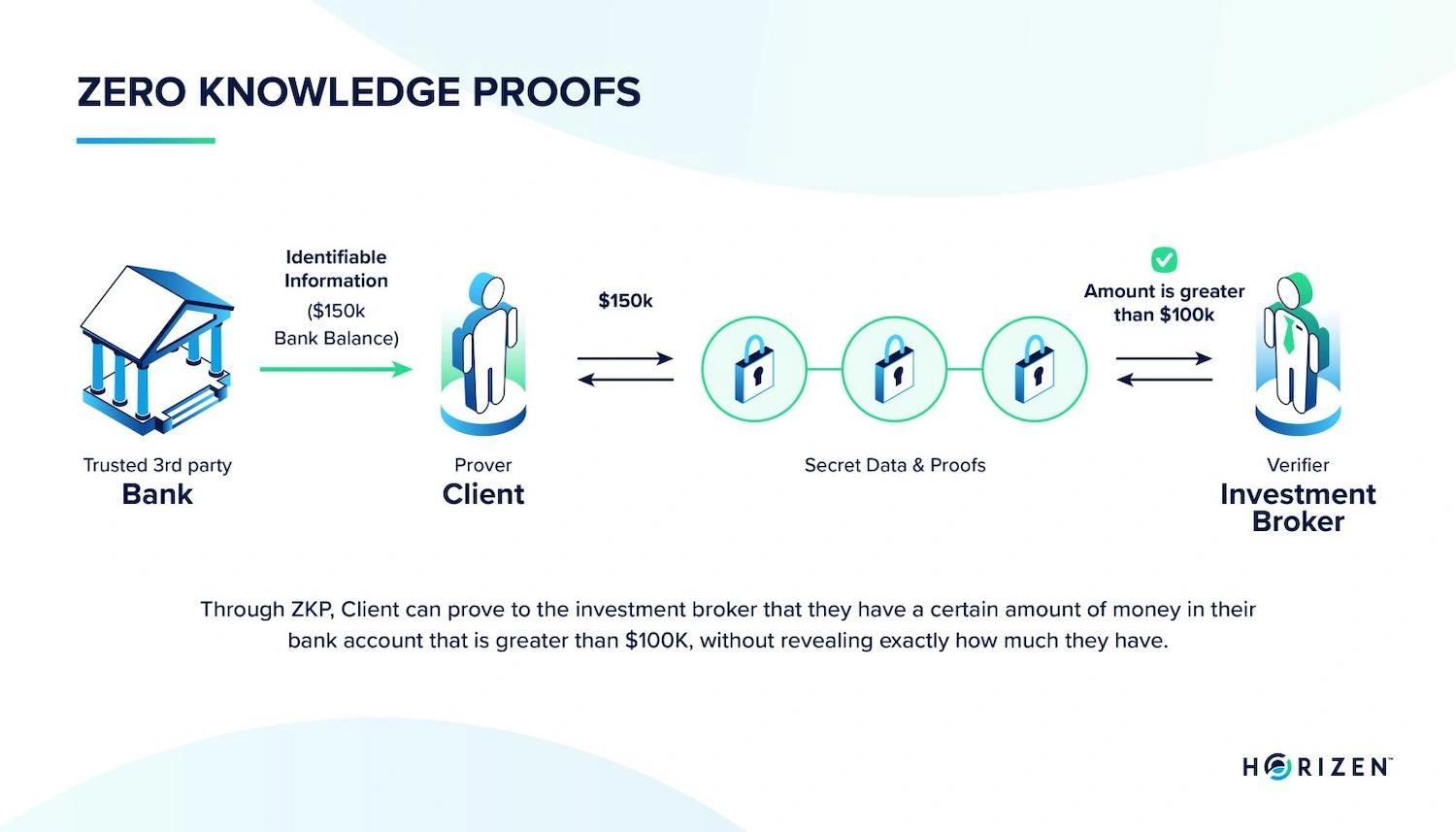
Zero-knowledge proofs are the mechanism that plays a crucial role in the development of modular blockchains. These cryptographic tools allow one party to prove a statement is true without revealing the underlying data.
(Source: Horizen)
On blockchains, ZK rollups process transactions off-chain. After this, this mechanism generates compact proofs that verify the computations were correct, and then it submits those proofs to Layer 1 for settlement.
There are many benefits of ZK proofs.
This allows end users to get quick finality. It can also reduce costs and increase throughput without compromising security.
The Ethereum Foundation’s Xiao-Wei Wang recently stated that zero-knowledge technologies are “the cornerstone of network evolution.” She said that years of research are finally creating real-world applications.
There are many developments taking place in 2026 in the ZK proofs sector. There is new hardware development through specialized chips and GPUs. These new developments have reduced proof generation times from minutes to seconds. This makes real-time applications useful.
Some popular projects like Polygon’s AggLayer are using recursive proofs. This sends proofs across many chains to concentrate liquidity. This helps creators to achieve throughput of over 100,000 transactions per second.
The Ethereum network is preparing for a major upgrade in the upcoming months. The next Glamsterdam upgrade in mid-2026 will shift validators to ZK proof verification. This will eliminate the need to re-execute transactions on Layer 1.
This could boost base throughput to 10,000 transactions per second while distributing the processing workload across different networks.
In the official post on X, Vitalik Buterin has stated the network could achieve major development by 2027 to 2030. zkEVM will become the main standard of validation across the ecosystem.
Popular Projects in ZK Rollup Space
The ZK rollups have grabbed many headlines as recently many projects rolled out. The zkSync Era is rapidly getting real-world adoption across numerous sectors. At the time of writing, zkSync is leading the total value locked with $5 billion, which provides account abstraction and full Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility. The platform is planning to introduce bank-grade privacy features through a system called Prividium. It hides sensitive data like balances and counterparties while still settling on Ethereum for security.
Starknet is using its Cairo Virtual Machine and STARK proofs to attract computationally intensive applications like gaming and AI. However, the network has also faced some challenges, including some outages. In January 2026, the network faced a bug in the blockifier component that caused a 4-hour network outage.
Another leading network is Polygon. Polygon zkEVM is working to achieve Ethereum standards to attract enterprises. On the other hand, Scroll is working on open-source development.
Conclusion
By late 2026 and in 2027, modular ZK chains are expected to become the major blockchain architecture. Also, Ethereum’s full ZK upgrade will help it to boost developments in the Web 3 sector and achieve the dream of “internet of blockchains.”
Another major development is LayerZero Labs, which recently launched Zero. It is calling it the first decentralized multi-core world computer. By using ZK proofs to take away execution from verification, the system is working on scaling it. All in all, this modular chain with a ZK proof mechanism is going to change the future of digital assets.
Also Read: Fungible Tokens vs Non-Fungible Tokens; Key Differences; Applications
See less